Annexation is a term used in international politics, history and law that refers to the process of forcibly annexing territory to an existing country. It is an action when one state incorporates the territory of another state into its own, changing the borders and political status of both countries. Usually, annexation is accompanied by the use of force, diplomatic pressure, or international treaties.
What is ANNEXATION – definition and meaning in simple words.
In simple terms, annexation is a process when one country, contrary to international law, annexes a part of the territory of another country by force.
In other words, it’s like when one neighbor takes a part of another neighbor’s garden and says that this land now belongs to him. Annexation has played a major role in history and international politics, and it is still a pressing issue.

Historical examples of annexations.
Numerous annexations have occurred throughout history. Some of them became famous and had a significant impact on the further development of world politics. Here are some of the most famous examples:
- The annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845: The motives were territorial, economic (resources and land), and political (support for American settlers in Texas). Consequences – confirmation of US dominance on the continent, outbreak of the Mexican-American War, change of US borders.
- Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014: Motives – imperialistic, strategic, political (control over the Black Sea, expansion of territories, expansion of demography). Consequences – international condemnation, sanctions against Russia, strengthening of separatism in eastern Ukraine, repression of the Crimean population, strengthening of Russia’s military presence in Crimea. Full-scale war between Russia and Ukraine.
- Annexation of the Golan Heights by Israel in 1981: Strategic and security motives (control over Israel’s main water resource, protection from Syrian aggression). Consequences – international condemnation, incomplete peace process between Israel and Syria, constant tension between the two countries.
- Annexation of Austria by Germany (Anschluss) in 1938: Motives – nationalist, political, economic (creation of Greater Germany). Consequences – the growth of Nazi Germany’s aggression, the outbreak of World War II.
- Annexation of Czechoslovakia by Germany in 1939: Motives – territorial, political, economic (military and industrial assets). Consequences – strengthening of Nazi Germany, aggravation of the international situation before World War II.
- Annexation of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania by the Soviet Union in 1940: Motives – strategic, imperialistic, political, expansion of the Soviet Union’s influence. Consequences – loss of sovereignty, repression, Stalinist policy.
- Annexation of Gibraltar by Great Britain in 1704: Strategic and political motives (control over Great Britain). Consequences – long-lasting territorial disputes between Great Britain and Spain.
- Annexation of Western Sahara by Morocco in 1975-1979: Motives – national, territorial, economic (phosphates). Consequences – a prolonged military conflict with the Polisario, international condemnation, instability in the region.
- Annexation of Tibet by China in 1950-1951: Motives – territorial, strategic, cultural (restoration of “historical China”). Consequences – loss of Tibetan sovereignty, cultural repression, international concern about human rights in Tibet.
- Annexation of Kuwait by Iraq in 1990: Motives – territorial, economic (oil resources), political (old territorial claims). Consequences – international condemnation, military operation “Desert Storm” with the liberation of Kuwait, economic and political sanctions against Iraq.
The motives and consequences of these annexations vary, but in general, they are carried out to expand territory, secure strategic advantages, or exploit natural resources. After annexations, the consequences include international condemnation, military conflicts, economic sanctions, and long-term tensions between countries.
It is important to note that international law prohibits the annexation of territories and offers other mechanisms for resolving territorial disputes.
Annexation is prohibited by a number of international laws and documents that form the basis of modern international law. The main ones are:
- The UN Charter (1945): This document enshrines the principles of territorial integrity and sovereignty of states. Article 2(4) prohibits the use of force or threat of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state.
- The Charter of the Organization of American States (1948): This document also enshrines the principles of territorial integrity and sovereignty of states in the Western Hemisphere.
- Geneva Conventions (1949): These four documents regulate the behavior of the parties during armed conflicts. They prohibit annexation, occupation, and other forms of unlawful alteration of territorial boundaries.
- Declaration on Principles of International Law concerning Friendly Relations and Co-operation among States (1970): This document, adopted by the UN General Assembly, prohibits acts of aggression, including annexation.
However, as historical examples show, annexations continue to occur and affect international politics and stability.
Analyzing the above examples of annexations, it is clear that they have different causes and consequences. However, what they have in common is the violation of international law, the sovereignty of states and the stability of the world order. In this regard, it is important to continue to uphold international norms and principles to prevent similar cases in the future.

Legal regulation of annexation.
Let’s take a look at the international laws and conventions that regulate annexation, consider the position of the United Nations on annexation, and explain how annexation can be justified or condemned from the point of view of law.
International laws and conventions.
International law contains a number of rules that regulate annexation and prohibit it in most cases. Documents such as the UN Charter, the Charter of the Organization of American States, the Geneva Conventions, and the Declaration on Principles of International Law establish the principles of territorial integrity and sovereignty of states.
UN position on annexation.
The United Nations has a clear position on annexation, which is expressed in the UN Charter. The UN strongly condemns annexation and calls on states to respect international law, including the principles of territorial integrity and sovereignty of states.
Legal justification and condemnation of annexation.
Although international law prohibits annexation in most cases, there are some situations in which annexation can be legally justified. For example, as a result of the voluntary retreat of the authorities of an integral state or during the peaceful resolution of a conflict through a real referendum rather than a plebiscite. However, in most cases, annexation is condemned by the international community as a violation of international law, which can lead to negative consequences for the annexing state and overall stability in the world.
Sanctions and liability for annexation.
Under international law, annexation may result in sanctions against the annexing state, which may take various forms, from political and economic restrictions to military operations. It is also possible to bring the leaders of the annexing states to justice before international judicial bodies, such as the International Criminal Court or a special tribunal.
In sum, annexation is a complex and controversial issue in international relations. International law prohibits annexation in most cases, but recognizes some exceptions. It is important to ensure compliance with international law and promote peaceful resolution of annexation conflicts to maintain international stability and security.
Annexation, integration, and cession – what is the difference?
Although annexation, integration, and cession are all related to the change of sovereignty over a territory, these concepts have differences and similarities in their processes and results. Let’s look at each of them.
- Annexation: As discussed earlier, annexation occurs when one state forces another state to alienate territory and annex it to its own, usually without the consent of the state from which it is being alienated. Case in point: Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014.
- Integration: Integration refers to the voluntary unification of territories when the population or government of a territory decides to join another state through a referendum or other legal process. Example: the integration of Germany in 1990.
- Cession: A cession occurs when one state voluntarily transfers part of its territory to another state, usually as part of an interstate agreement or as a result of a peace treaty. Example: the cession of Louisiana to the United States by France in 1803.
Thus, the main differences between these concepts are the voluntariness and the method of transferring the territory. Annexation is usually considered illegal, while integration and cession are based on legal processes and international consent. On the other hand, the similarities between them are that they all involve a change of sovereignty over a territory.
Additional examples to illustrate each concept:
Annexation
- The annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina by Austria-Hungary in 1908.
- The annexation of South Ossetia and Abkhazia by Russia in 2008.
Integration
- Integration of Hawaii into the United States in 1959.
- Integration of the two Yemenis in 1990, when South Yemen and North Yemen united to form modern Yemen.
Cession
- The cession of Alaska to the United States by the Russian Empire in 1867.
- The cession of Hong Kong to the United Kingdom by China in 1842 as a result of the First Opium War (Hong Kong was returned to China in 1997).
All of these examples demonstrate the differences and similarities between annexation, integration, and cession.
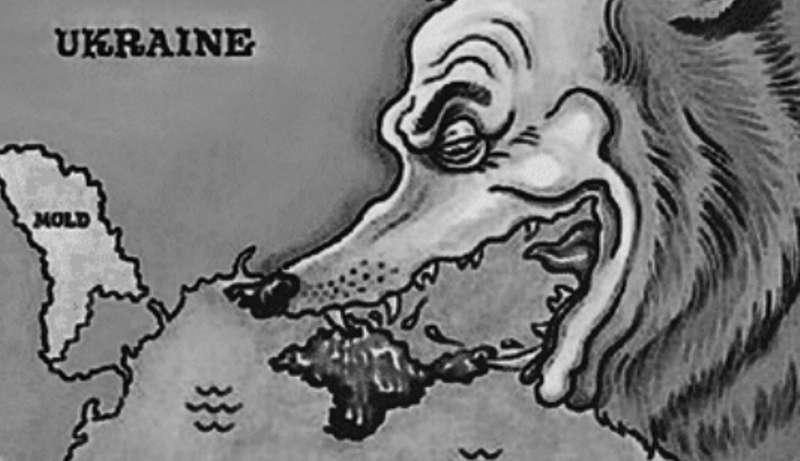
Modern annexation and its consequences.
Annexation continues to play an important role in contemporary global politics, particularly in terms of international relations and compliance with international law. Modern cases of annexation, such as Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014, as well as attempts to annex other territories of Ukraine during Russia’s full-scale invasion (February 24, 2022), have caused significant international tensions and changed the balance of power on the world stage.
Potential consequences of the annexation for international relations include escalation of conflicts, sanctions, embargoes, and a ban on cooperation with aggressor countries, which could lead to isolation and economic decline. In addition, annexation can lead to interethnic and interfaith conflicts in the annexed territories, violating human rights and creating humanitarian crises.
Realizing the global consequences of annexations, the international community and UN member states seek to prevent such cases through dialogue, diplomacy, and international judicial decisions. Sometimes, however, conflicts cannot be resolved purely peacefully, especially when the aggressor is not going to give up its goals. In such cases, the community must resort to more severe and decisive actions to punish the violator of international law.

Why can’t annexation be justified by the right of people to self-determination?
Annexation cannot be justified by the right to self-determination for several reasons:
- Difference of principles: The right to self-determination is based on the principle of respect for the will of the people, some communities have the right to determine their political status and freely develop their economic, social and cultural system without changing the borders of the country. Annexation, on the other hand, is the forcible seizure of territory from one state by another, and often goes against the will of the people.
- International law: The right to self-determination is recognized by international law, in particular in Article 1 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and Article 1 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights. In contrast, annexation is prohibited under international law, especially in light of Article 2(4) of the UN Charter, which prohibits the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state.
- Consequences for the population: The right to self-determination protects the interests of the people by allowing them to choose their own path of development without external interference. Annexation, on the other hand, can have negative consequences for the population, violating their rights, creating suffering and causing instability.
- Decision-making process: The right to self-determination, subject to international law, can be exercised through peaceful processes such as referendums, negotiations between the parties, and dialogue with the international community. In such cases, the results reflect the democratic choice of the people, taking into account their interests and rights. Annexation, on the other hand, usually occurs as a result of military aggression or political coercion, without due regard for the will of the population and international law.
- Impact on international relations: The right to self-determination promotes peaceful coexistence among peoples and cooperation between states. However, annexation can lead to international conflicts, violations of international law, and even wars, which can have far-reaching consequences for the stability and security of the region and the world as a whole.
Thus, annexation cannot be justified by the right to self-determination for a number of reasons, such as differences of principle, violations of international law, negative consequences for the population, and consequences for international relations. The right to self-determination is realized through peaceful processes aimed at protecting the interests of the people, while annexation is a forcible seizure of territory and takes place without regard to the will of the people.
It is important to emphasize:
In the situation of Russia’s war against Ukraine, Russia often manipulates the concept of the people’s right to self-determination. However, this cannot serve as a justification for aggression and annexation, as Russians as a nation already have their own large country with their own borders. They have long since defined themselves as a nation and can always return to their homeland if they wish, rather than tearing a piece of territory away from another country.
Annexation and Occupation: Interrelation and Differences.
Annexation and occupation are two concepts of international law related to the change of control over a territory, but they differ in their goals, mechanisms, and consequences.
- Annexation is an act by which one state legally incorporates the territory of another state into its borders, usually without taking into account the will of the population of that territory. Annexation can occur as a result of war, political coercion, or diplomatic agreement. Annexation is a violation of international law, in particular the principle of inviolability of borders and the prohibition of the seizure of territory by force.
- Occupation is the temporary military occupation of the territory of one state by another state without the transfer of sovereignty. Occupation can occur during a war or armed conflict when the aggressor state deploys its troops on the territory of another state and exercises control over this territory. International law regulates occupation through documents such as the Geneva Conventions, which establish rules for the treatment of occupied territory and its population.
The relationship between annexation and occupation is that both processes involve a change of control over a territory, but there are important differences.

Annexation and occupation – what is the difference?
- Duration: Annexation involves the permanent incorporation of a territory into the annexing state, while occupation is a temporary phenomenon.
- Status of sovereignty: In the case of annexation, the annexing state takes away sovereignty over the territory by changing national borders. In the case of occupation, the sovereignty of the occupied state is formally preserved, and control is temporary.
- International law: Annexation is generally considered a violation of international law, while occupation, while it may have negative consequences, is regulated by international treaties such as the Geneva Conventions.
- Relations with the population: Annexation often takes place without taking into account the will of the population of the territory, while during occupation, international law requires that the rights of the population of the occupied territory be respected.
- Responsibility to the international community: In the case of annexation, the annexing state may face international sanctions and isolation, while in the case of occupation, the occupying state is obliged to comply with international agreements and norms governing behavior during occupation.
It is worth noting that these international norms, which the aggressor state must comply with during annexation or occupation, are usually not observed. Repression and war crimes are usually committed in the annexed or occupied territories.

FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions):
Annexation is a process where one state conquers the territory of another state and incorporates it into its own. This is prohibited by international law.
Annexation is the illegal appropriation and incorporation of the territory of another state by one state. Occupation is the temporary military control of a territory without the transfer of sovereignty. The difference is that annexation implies a permanent merger of territories, while occupation is temporary control without changing national status.
The annexation of Crimea means the illegal seizure of the territory of Crimea by the Russian Federation in 2014, which violated international law.
The term “annexation” means the illegal conquest of the territory of one state by another state.
No, annexation is prohibited under international law, in particular the UN Charter.
Annexation is the illegal conquest of territory, integration is the voluntary unification of territories, and cession is the transfer of territory from one state to another on the basis of an international treaty.
The right to self-determination implies the free choice of the people of their political system and status. Annexation, as an illegal conquest, violates this right, as it forcibly imposes a new status on a territory without the voluntary consent of the population.
Theoretically, annexation can occur peacefully through the voluntary consent of both parties, but such cases are rare in history. Usually, annexation is considered a violation of international law, regardless of the nature of the interaction between the states.
Yes, an annexation can be canceled through international agreements, negotiations, or as a result of a change in the political situation. Reversal of an annexation may involve returning the territory to the previous sovereign or changing its status.
Annexation can have a significant impact on the lives of the local population, which may include a change in nationality, loss of political rights and freedoms, discrimination on linguistic and ethnic grounds, changes in legislation and administrative structure, and economic impacts such as loss of jobs, increased poverty, or changes in land ownership.




